The Battle of New Market Heights: the 5th USCT’s “Glory”
Wednesday, September 24th, 2014by Ron Gorman, Oberlin Heritage Center volunteer docent
150 years ago this week, an important, but often overlooked, battle was fought in the American Civil War. It was the Battle of New Market Heights, fought September 29, 1864, on the outskirts of the Confederate capitol of Richmond, Virginia. It was important because it showcased a new strategy that Union General Ulysses S. Grant would employ successfully against Confederate General Robert E. Lee – a strategy that involved, in part, the use of African American soldiers. With 180,000 African American soldiers joining the Union cause in the last two years of the war, this was a significant morale boost for the Union, and a bad omen for the Confederacy. It was also an important battle for Ohio, as the victory was led by Ohio’s first African American regiment, the 5th United States Colored Troops (USCT) infantry. And it was especially important to Oberlin, whose influence and presence pervaded the 5th USCT.
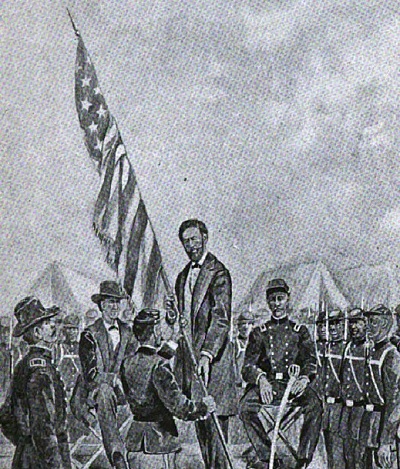

John Mercer Langston presents the colors to the 5th USCT
That influence began with Oberlin’s John Mercer Langston. When Congress passed legislation in 1862 that allowed African Americans to serve in the United States army for the first time in decades, Langston volunteered to recruit an Ohio regiment. But Ohio Governor David Tod told Langston that “to enlist a negro soldier would be to drive every white man out of the service.” Meanwhile black regiments were recruited in other states, and Langston and his Oberlin brother-in-law, Orindatus S. B. Wall, helped recruit the 54th Massachusetts Infantry, which included 18 Oberlin men and would be immortalized in the 1989 movie “Glory”. Finally, in June, 1863, Governor Tod gave Langston and Wall the go-ahead to recruit Ohio’s own black regiments. They diligently set about recruiting African Americans from all over Ohio, including four more men from Oberlin. These men enlisted in the 127th Ohio Volunteer Infantry, which eventually was renamed the 5th United States Colored Infantry. [1]
Although racial tabboo dictated that the regiment be led by white officers, Langston knew the perfect candidate for its commander, “a young man of extraordinarily high personal and social character, of strictly Christian principles and habits, with recognized reputation and influence as an abolitionist and friend of the negro race”, Oberlin’s Giles W. Shurtleff. Shurtleff had served earlier in the war as Captain of the “Monroe Rifles” (see A Fond Farewell and Oberlinians’ First Battle of the Civil War). When informed of his nomination, Shurtleff wrote his future wife, “I do not seek the appointment but am willing to take it if I can be of service to the country and to the blacks.” But Shurtleff was appointed assistant commander, with a commission as Lieutenant Colonel, instead. Several other white Oberlinites would also secure officer’s positions in the regiment, including James B. T. Marsh (quartermaster, and former publisher of the abolitionist Lorain County News), Elliott Grabill (adjutant), and John Patton (chaplain). [2]
The regiment was mustered into service in November, 1863 and attached to the “Army of the James”, operating in the James River watershed of eastern Virginia. There they would see much more action than their sister Ohio regiment, the 27th USCT (see my Battle of the Crater post), due largely to the Army of the James’ controversial commander, Major General Benjamin Butler, who had become one of the army’s strongest advocates of the abilities of the black troops. And so the 5th USCT immediately began launching raids in coastal Virginia and North Carolina, capturing guerillas, destroying Confederate supplies, and freeing slaves. [3]
In June, 1864, when General Ulysses S. Grant launched the Army of the Potomac against the Confederate rail hub of Petersburg, just south of Richmond (see my Battle of the Crater blog), the 5th USCT participated in the initial assault on its sparsely manned defenses. Together with several other USCT regiments, they captured Confederate entrenchments, artillery positions and cannon. With proper reinforcement they would have been in a prime position to capture Petersburg itself. But the commanding general on the field hesitated, and to Shurtleff’s great frustration, “the next day there were confronting us instead of 2,200 of Wise’s Militia and convalescents of the previous evening, 10,000 veterans with bristling bayonets and a hundred cannon mouths all behind strong breastworks and formidable redans; and during the next three days 10,000 brave soldiers were sacrificed in fruitless assaults…” Thus began a 9 month siege of the city of Petersburg. [4]
Nevertheless, the news of the success of the 5th USCT and their fellow African American regiments spread far and wide. President Lincoln himself expressed “the greatest delight” with “how gallantly they behaved” and accepted General Grant’s invitation to review them a few days later. According to Lieutenant Grabill, “the colored men lined both sides of the road and cheered” as Lincoln and Grant rode by. An aide to General Grant reported, “the President rode with bared head; the tears had started to his eyes, and his voice was so broken with emotion that he could scarcely articulate the words of thanks and congratulations with which he tried to speak to the humble and devoted men through whose ranks he rode.” [5]
In fact, the accomplishment of Butler’s USCT regiments during the initial assault on Petersburg helped inspire General Ambrose Burnside’s decision to have his own USCT regiments spearhead the assault at the Battle of the Crater six weeks later. Interestingly, the 5th USCT, now assigned to duty in the Petersburg trenches, would have a ringside seat for that battle, helplessly watching the “unspeakable stupidity” (in Shurtleff’s words) of the management of that battle, and suffering 14 casualties to friendly fire in the process. [6]
The Battle of the Crater appears to have finally convinced Grant of two things: the futility of storming heavily manned entrenchments head-on (with or without the help of explosive-laden underground mineshafts), and the fighting mettle of the USCT soldiers. So now he embarked on a new strategy in which the USCT regiments would play a crucial role. In late August, the 5th USCT was pulled out of the Petersburg trenches and sent to the banks of the James River on the outskirts of Richmond, where they were to prepare for an upcoming offensive. Grant was going to hit Lee with a one-two punch at both ends of his line simultaneously.
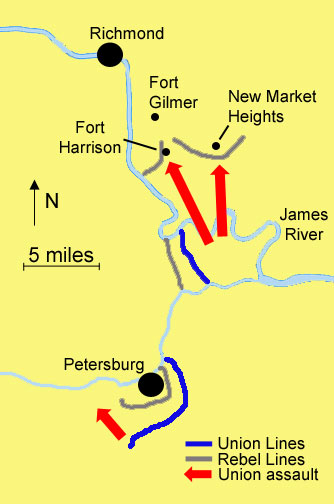
The Army of the James would attack the northern end of the Confederate line at the heavily fortified but lightly manned outskirts of Richmond. Grant hoped that they could gain a foothold on the James peninsula and draw enough Confederate reinforcements away from Petersburg so his attack at the south end of the line could succeed as well. Butler devised a strategy for a two-pronged attack against the Richmond defenses, with the western prong (comprised mostly of white soldiers) attacking Fort Harrison, and the eastern prong (comprised of two white divisions and two black divisions) attacking a formidable position called New Market Heights.
The attack began at dawn on September 29, 1864. While the western prong made solid gains against the defenses surrounding Fort Harrison, the eastern prong got off to an inauspicious start. The consensus among military historians is that the generals commanding this prong fed their troops in piecemeal, negating their huge numerical advantage. To make matters worse, the troops had to advance across extremely difficult terrain under fire from what one military historian called “among the best [infantry] in the Army of Northern Virginia.” The 4th USCT and 6th USCT regiments spearheaded this assault. In forty minutes of grueling fighting a few of these soldiers actually succeeded in breaching the Confederate entrenchments, but not enough to take the position. Ultimately they were driven back with heavy casualties. [7]
At 8:00 AM the Union command made a second attempt, but again using the same piecemeal approach. This time the 5th USCT, now under the command of Colonel Shurtleff, would lead the advance over the same terrain where the 4th and 6th USCT had just been so disastrously repulsed. Exhorting his troops to erase the “stigma” of “cruel prejudice and oppression”, Shurtleff led them onto the battlefield. The regiment had to ford a stream and slog their way through marshy bottomlands and over the bodies of their fallen comrades, during which time Shurtleff noted that enemy artillery “poured in upon us with incessant fury.” One Confederate recounted that as the USCT troops advanced upon them, “they shouted remember ‘Fort Pillow’ & give the Rebels no quarter. This stirred up our men and everybody seemed mad for the first time.” Shurtleff observed that “the enemy’s infantry opened moderately upon us, and shouted in defiance and derision, ‘Come on, you smoked yankees, we want your guns’.” [8]
But this was the easy part. Climbing the slope out of the marshes, the troops encountered two lines of enemy obstructions called “abatis”. At this point, Shurtleff noted, “our progress was arrested, and the most murderous fire that I witnessed during the war opened upon us.” (Coming from a man who had witnessed first-hand the carnage of the Battle of the Crater and the Battle of Fredericksburg, this statement carries some weight.) Shurtleff himself was struck by a rebel bullet in the hand, but receiving no order to retreat, he commanded his men “Forward, double quick”, at which time he “received a second wound in the thigh which rendered me insensible for perhaps 15 minutes.” [9]

“Chevaux-de-frise” – one of the lines of “abatis” that the USCTs had to get past
Shurtleff was one of several 5th USCT officers taken out by enemy fire. Four of the regiment’s ten companies suddenly found themselves without any officers to guide them. In such circumstances, Civil War soldiers would often break into panicked retreat. But four sergeants, all African American, now stepped up to take command of their leaderless companies and rally them forward. However such grit and determination, against such galling fire, would likely have resulted only in scattering the bodies of more USCT heroes over the battlefield if it weren’t for another concurrent development.
At about the same time the 5th USCT began its advance, the Confederate commander, under heavy assault at Fort Harrison, requested reinforcements from the New Market Heights line. So now, as rebel soldiers were systematically pulled out of the New Market Heights defenses, the amount of fire greeting the advancing USCT troops gradually diminished, until at some point it dwindled to a level where the sheer determination of the USCT troops was able to overcome it. (There is considerable disagreement among military historians about the exact timing and scope of this. [10]) At that point, the 5th USCT, followed by two other USCT regiments, swarmed through the abatis and over the Confederate parapets. And so it was that Colonel Shurtleff regained consciousness just in time to see his troops “chasing the rebels over a hill a quarter of a mile beyond the works they had captured.” [11]
Although a Confederate soldier would later write that “Richmond came nearer being captured, and that, too, by negro troops, than it ever did during the whole war”, the Rebels weren’t about to give up. The Confederates had an “intermediate” line of entrenchments located about 4 miles in the rear. This line was now manned by rebel soldiers who had been driven out of New Market Heights and Fort Harrison, which had been overrun by Butler’s western prong. By the time the Union troops regrouped to attack these defenses, they were already being reinforced with troops sent from Richmond and Petersburg by Confederate General Robert E. Lee. The 5th USCT, already decimated at New Market Heights, would now be called on again to shed even more blood assaulting the lynchpin of these works at Fort Gilmer, but were unable to repeat their earlier success. It became clear that the Army of the James had gone as far as it could and now would have to hunker down to hold the territory it had gained. This it would do, despite the arrival of General Lee to personally direct Confederate attempts to retake that ground. [12]
The transfer of Confederate reinforcements from Petersburg to Richmond also aided in the success of the southern portion of Grant’s one-two punch. Union troops there were able to capture territory up to two miles beyond the existing lines. The Union gains at both ends of the line forced the Confederates to lengthen their own lines and spread their dwindling manpower even thinner. Just three months later, Robert E. Lee would become so desperate for manpower that he would propose a “plan of gradual and general emancipation”, explaining that “we must decide whether slavery shall be extinguished by our enemies, and the slaves be used against us, or use them ourselves at the risk of the effects which may be produced upon our social institutions. My own opinion is that we should employ them without delay.” And just three months after that, Lee’s thin lines would break completely and USCT troops would march into Richmond. [13]
But the New Market Heights victory didn’t come cheap. The 5th USCT lost 236 men that day – killed, wounded, captured, and missing – out of the 540 they started with. Among the killed were Oberlin’s Henderson Taborn and James Matthews, both of whom had to be left severely wounded on the battlefield (presumably at Fort Gilmer, where the Confederates retained control of the ground). Taborn, a cabinet maker and father of five, was reported seen “after his death” by “comrades who were taken prisoner at the time of the assault.” But nothing further was ever heard of Matthews, who, when recruited, had told Langston of “his desire to have his [pregnant] wife and also his child when born well provided and cared for” in his absence. His military file states that he was captured and killed by the rebels, but this appears to be speculation. Although there were credible reports of Confederates killing black captives, the slaughter wasn’t nearly as widespread as it had been at the Battle of the Crater, and some wounded black prisoners were treated at Richmond hospitals and even survived the war. But whether Matthews died of his battle wounds or something more sinister, the young man who had “expressed great tenderness” for his pregnant wife would never see his baby daughter. [14]

Matthews and Taborn: Oberlin Soldiers’ Monument
Several surviving soldiers of the 5th USCT, including Colonel Shurtleff, were awarded promotions for their heroism at New Market Heights and Fort Gilmer. Milton Holland, one of the African American sergeants who took command of his company on the field, was awarded a battlefield promotion to captain by General Butler, only to have it rescinded by the War Department on account of Holland’s race*. So instead Butler awarded a newly issued medal to Holland and the three other 5th USCT sergeants who led their companies, along with 10 other black soldiers from his other regiments. (Although none of these men were from Oberlin, Robert Pinn attended Oberlin College after the war). This new medal was the “Medal of Honor”. Little did anyone realize at the time how prestigious this medal would someday become, but I think the full prestige of this award today is well deserved by these men for their heroic struggle in two battles simultaneously – one against the Confederate army, and the other against the “cruel prejudice and oppression” that pervaded both armies. [15]

*NOTE: It was reported that Governor Tod advised Holland that his promotion could be reinstated if he would deny his African ancestry. Holland refused. [16] Two bills have recently been introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives (H.R. 3364 and H.R. 3412) to posthumously reinstate the rank of captain to this Medal of Honor recipient.
In my next and final blog in this Civil War sesquicentennial mini-series, I’ll tell the story of Oberlin’s own recipient of the Medal of Honor during the Civil War.
Sources Consulted:
Versalle F. Washington, EAGLES ON THEIR BUTTONS: A BLACK INFANTRY REGIMENT IN THE CIVIL WAR
James S. Price, The Battle of New Market Heights
Giles W. Shurtleff, “Reminiscences of Army Life”, Oberlin College Archives, RG 30/032, Series 7, Subseries 1, Box 1, “Writings re the Civil War”
Catherine Durant Vorhees, The Colors of Dignity
Richard J. Sommers, Richmond Redeemed: The Siege at Petersburg
Official Records of the Rebellion (abbrev. “O.R.” below), Series 1, 4
William E. Bigglestone, They Stopped in Oberlin
Oberlin College Archives (abbrev. “O.C.A.” below), RG 30/151, Series I, Subseries 1, “William E. Bigglestone Papers; Files Relating to They Stopped in Oberlin; Civil War Military Records”
John Mercer Langston, From the Virginia Plantation to the National Capitol
Richard Slotkin, No Quarter: The Battle of the Crater, 1864
Charles Bracelen Flood, 1864: Lincoln at the Gates of History
Connie Perdreau, A Biographical Sketch of Master Sergeant Milton Holland, Gen. Charles H. Grosvenor Civil War Round Table
“Civil War Soldiers and Sailors Database”, National Park Service
General Catalogue of Oberlin College, 1833 [-] 1908, Oberlin College Archives
“Great Fighting about Richmond”, Lorain County News, October 5, 1864, p. 3
George Washington Williams, A History of the Negro Troops in the War of the Rebellion
James M. Guthrie, Campfires of the Afro-American
Footnotes:
[1] Langston, p. 206; Washington, pp. 7-9; Bigglestone, p. 237
[2] Langston, p. 209; Voorhees, p. 102
[3] Washington, pp. 33-34
[4] Washington, pp. 42-43; Shurtleff, p. 13
[5] Vorhees, p. 129; Flood, pp. 155-156
[6] Shurtleff, pp. 31-34
[7] Sommers, p. 34
[8] Washington, p. 53; Shurtleff, pp. 37-38; Price, p. 71
[9] Shurtleff, pp. 38-39
[10] Sommers, p. 38; Price, pp. 69-70,77-78, 87-89; Washington, pp. 56-57
[11] Shurtleff, p. 41
[12] Price, p.86
[13] O.R., Series 4, Vol 3, Part 1, p. 1013
[14] Washington, pp. 53, 59, 60, 89-90; Bigglestone, pp. 147, 196, 238; Affidavit (G. W. Shurtleff), “Taborn, Henderson” file, O.C.A., Bigglestone Papers, Box 3; Sommers, p. 35; Memorandum (Adjutant General’s Office, Nov 4, 1869), “Matthew, James” file, O.C.A., Bigglestone Papers, Box 2
[15] O.R., Series 1, Vol 42, Part 3, p. 168; General Catalogue, p. 771; Voorhees, p. 191
[16] Perdreau